Specially created this article for members of ERG onlyHow To Easily Understand The Functions Of Switch Mode Power Supply
If there is a problem in the linear transformer circuit, I can say that it is very easy to locate the fault. This is somehow different in the case of a switch mode power supply. The designs were complicated and some technicians found it quite hard to fully understand how the switch mode power supplies work.
The clean DC voltage will then flows to start up resistors and to the input of switch mode power transformer. Once the voltage passed through the high ohms resistor (start up resistors) the voltage would drop to a value where it then flows to the VCC supply pin of Pulse width modulation IC.
Once the PWM IC received the voltage it will output a signal to drive the transistor (or FET) and produces a changing in magnetic field in the transformer primary winding. The changing magnetic field induces voltage in the secondary windings.
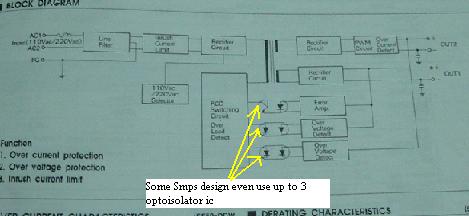
The output from the B+ voltage supply is then connected, through a “feedback” loop (which consist of optoisolator ic and an error amplifier TL431 IC), back to the PWM IC. When the voltage from the B+ supply rises or drop a bit, the PWM IC will act to correct the output.
If you still do not understand the above explanation, please do not be discourage because you can always buy technical books and schematic diagrams and read it till you get the whole idea of how a SMPS work. You can ask a repair friend or even surf the internet for a better and easy explanation.
Here's a free download of SMPS article by Sencore and I found it to be a great help for you who are still struggle on how SMPS work and how to troubleshoot when it fails. You must ask your self what is the purpose and its function of the components in the SMPS circuit and how to check them if they fail. Find out on your own the function of these components in SMPS circuit:
Bridge rectifier, Filter capacitor, Start up resistors Chopper/Power FET Pulse Width Modulation (PWM IC) Current sense resistor Switch mode power transformer Optoisolator/optocoupler Error Amplifier IC (TL431) Secondary diodes Secondary filter capacitors
Push yourself further by searching the internet for the datasheet of a PWM IC part number. For example, UC3842 PWM IC is mostly used in SMPS. Do you know what the function of pin 5 of this IC is? Do you know which pin the VCC supply enters? Do you know what the actual voltage that flow to the IC is? Do you know which pin that drives the power FET? Can I get a replacement for this IC? And so on………
Let’s take a soldier as an example. Soldiers not only good in handling rifle but also knows all the details about it. They know how to dismantle and assemble back their rifle fast (imagine in the middle of war the rifle jammed-they can repair it fast). They know how much each bullet cost, how far the shooting distance, how big is the diameter of the bullet, how many cm the length of the bullet and so on. Hope you don’t get bored with the soldier’s story, did you get the ideas?
Any SMPS that comes across my repair bench, I would not immediately repair it, in fact I will take couples of minutes to analyze the circuit design and see it from all angles before I begin to repair. Troubleshooting SMPS is not limited to only one procedure in fact many electronic repairers have their own unique ways and methods to solve SMPS problems. Some prefer to use light bulb to isolate SMPS faults while others like to use resistors. Troubleshooting SMPS is fun and flexible but in some cases could make you get very frustrated too.
Remember, don’t limit yourself to only one or two sources to get you understand and be able to repair SMPS. If you have the budget, get the books that have related to SMPS repair-study and start doing practical about it. Share your problems with other fellow electronic repairers and the most important thing is don’t give up. There’s lot of mountain in the journey of our live and you yourself have to climb and conquer it. All the best!
|
|
Copyright@ 2006-2014-www.ElectronicRepairGuide.com All Rights Reserved

 Troubleshooting linear power supply was quite easy as compare
to switch mode power supplies (SMPS). AC voltage enters to the
primary side of linear transformer and then converted the AC into a
lower or higher AC voltage depending on the secondary winding. The
output AC voltage is then rectified and filtered by a diode and
capacitors to produce a clean DC voltage.
Troubleshooting linear power supply was quite easy as compare
to switch mode power supplies (SMPS). AC voltage enters to the
primary side of linear transformer and then converted the AC into a
lower or higher AC voltage depending on the secondary winding. The
output AC voltage is then rectified and filtered by a diode and
capacitors to produce a clean DC voltage. The working
principle of switch mode power supply is different from the linear
type. First the AC voltage will flow to a full wave rectifier
(bridge rectifier) which produces an uneven DC output and then
filtered by a large capacitor (usually 220 micro farad and up to
450 volts).
The working
principle of switch mode power supply is different from the linear
type. First the AC voltage will flow to a full wave rectifier
(bridge rectifier) which produces an uneven DC output and then
filtered by a large capacitor (usually 220 micro farad and up to
450 volts).  Each of these AC voltage produced by the secondary
windings is then rectified, filtered, and regulated to produce
a clean DC voltage. One of the main DC output voltage is the
B+ that supply to flyback transformer (for TV and Monitor
Circuit)
Each of these AC voltage produced by the secondary
windings is then rectified, filtered, and regulated to produce
a clean DC voltage. One of the main DC output voltage is the
B+ that supply to flyback transformer (for TV and Monitor
Circuit)